Alzheimer’s disease is a growing public health crisis in the United States. In 2025, the burden of Alzheimer’s disease continues to rise, impacting millions of Americans, their families, and the healthcare system.
According to the Alzheimer’s Association, approximately seven million Americans aged 65 and older are currently living with Alzheimer’s dementia, and this number is expected to increase dramatically in the coming years.
Table of Contents
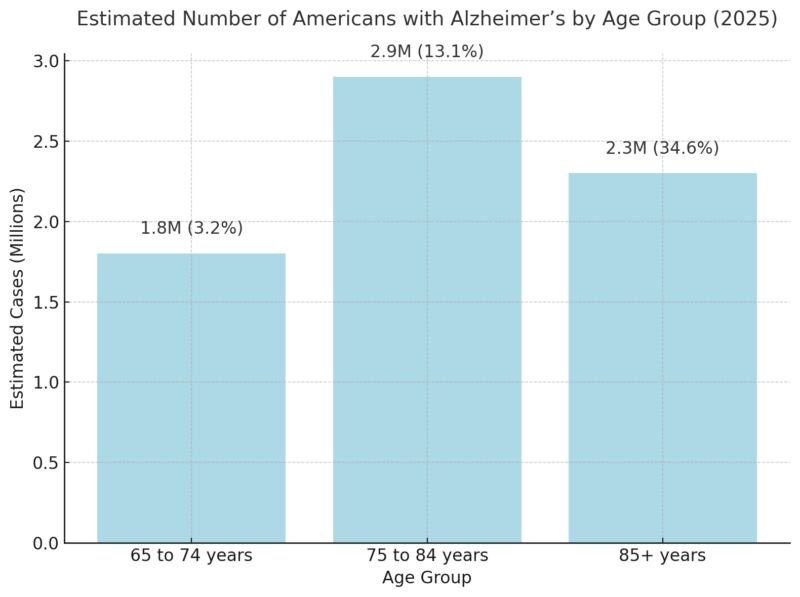
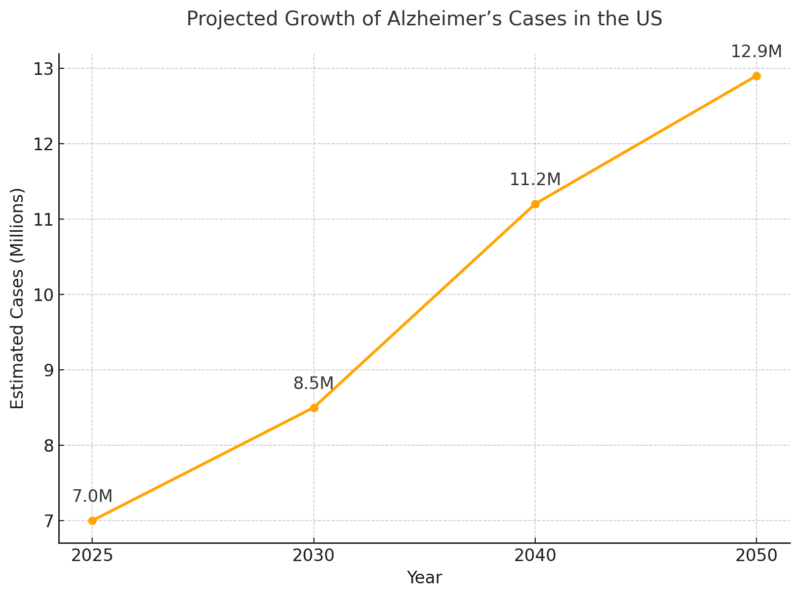
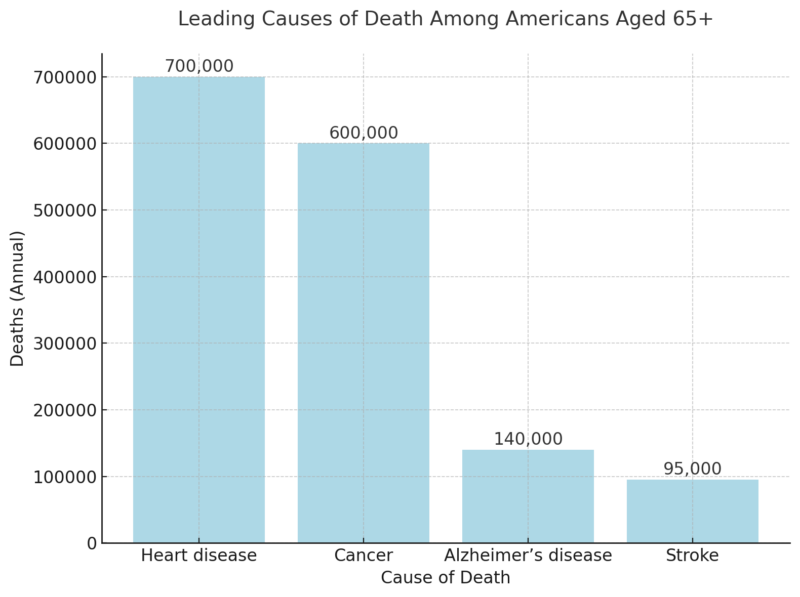
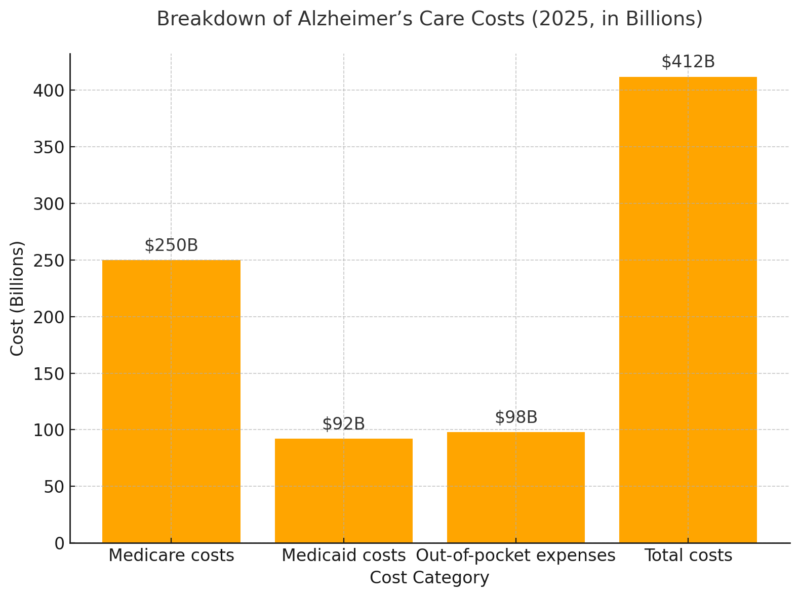
ToggleThe number of Americans diagnosed with Alzheimer’s is steadily increasing. Below is an overview of Alzheimer’s prevalence by age group in 2025: Alzheimer’s disproportionately affects older adults, with over 73% of cases occurring in individuals aged 75 or older. The 34.6% prevalence rate among those aged 85 and older underscores the importance of early intervention. Given that Alzheimer’s begins developing years before symptoms appear, targeted lifestyle and medical interventions in middle age (50s and 60s) could help delay or reduce future cases. Additionally, the disease impacts women at nearly twice the rate of men, which is partially attributed to longer life expectancy and potential hormonal and genetic factors. Recent studies indicate that alternative and holistic approaches may also play a role in cognitive health. Exploring lifestyle changes, dietary habits, and natural health solutions has become increasingly popular. Some patients are also turning to medical marijuana as a potential way to manage symptoms, with platforms like Leafy Doc connecting individuals with licensed doctors for medical cannabis evaluations. While some research suggests cannabis may provide symptom relief, experts caution that it could also contribute to cognitive decline in older adults, making professional medical guidance essential before considering it as a treatment option. By 2050, the number of Americans aged 65+ living with Alzheimer’s is projected to reach nearly 13 million according to ALZ. Key drivers of growth: Aging population, longer life expectancy, and increasing risk factors. Alzheimer’s is among the leading causes of death in the United States. Between 2000 and 2025, deaths from Alzheimer’s increased by 145%, while deaths from heart disease and stroke have declined as noted by NIH. Alzheimer’s shortens life expectancy significantly. At age 70, individuals diagnosed with Alzheimer’s are twice as likely to die before age 80 compared to those without the disease. Alzheimer’s disease imposes a massive financial burden on families and the U.S. healthcare system. The total annual cost of care for people with Alzheimer’s in 2025 is projected at $412 billion. The $412 billion cost of Alzheimer’s care demonstrates the massive financial burden this disease places on individuals, families, and the government. Medicare and Medicaid bear 75% of these expenses, showing how dependent dementia patients are on public funding. Out-of-pocket costs ($98 billion) also indicate that families are shouldering an increasing financial burden, particularly in home care and long-term facility expenses according to NCBI. As cases rise, costs are projected to surpass $1 trillion by 2050, creating an unsustainable economic situation unless preventive measures, better treatments, and caregiver support programs are expanded. Alzheimer’s doesn’t just affect those diagnosed; it also places immense stress on caregivers. Nearly two out of three caregivers are women, and over 30% are daughters of those they care for according to this Alzheimer’s report. 40% of caregivers report suffering from clinical depression or high stress due to caregiving demands. The demand for healthcare professionals specializing in Alzheimer’s care is increasing rapidly. Despite advancements, no cure for Alzheimer’s exists. The search for new treatments, prevention strategies, and diagnostic tools remains critical. If an effective treatment is discovered by 2030, it could save the U.S. $500 billion in healthcare costs. More than $3.8 billion in federal funding is being invested in Alzheimer’s research in 2025. This article was crafted using data-driven insights from the Alzheimer’s Association 2025 Facts and Figures Report, combined with supporting statistics from organizations like NIH and NCBI. We analyzed prevalence rates, financial costs, mortality trends, and caregiving burdens to present a comprehensive view of Alzheimer’s in the U.S. The data was structured into detailed tables for clarity, with additional expert analysis beneath each dataset. All figures were cross-referenced with official public health sources to ensure accuracy. Finally, the article was designed to be accessible and informative for a broad audience, including caregivers, policymakers, and healthcare professionals.Key Takeaways
Prevalence of Alzheimer’s Disease
Estimated Number of Americans with Alzheimer’s by Age Group
Projected Growth of Alzheimer’s Cases
Projected Growth of Alzheimer’s Cases in the US
Mortality and Impact on Lifespan
Leading Causes of Death Among Americans Aged 65+
Financial Costs of Alzheimer’s Disease
Breakdown of Alzheimer’s Care Costs (2025, in Billions)
The Burden on Caregivers
Caregiving Burden for Alzheimer’s Patients
Category
Statistic
Total number of caregivers
11.5 million
Unpaid care hours provided
19.2 billion hours
The economic value of unpaid care
$420 billion
% of caregivers reporting stress
60%
% of caregivers who had to leave jobs
22%
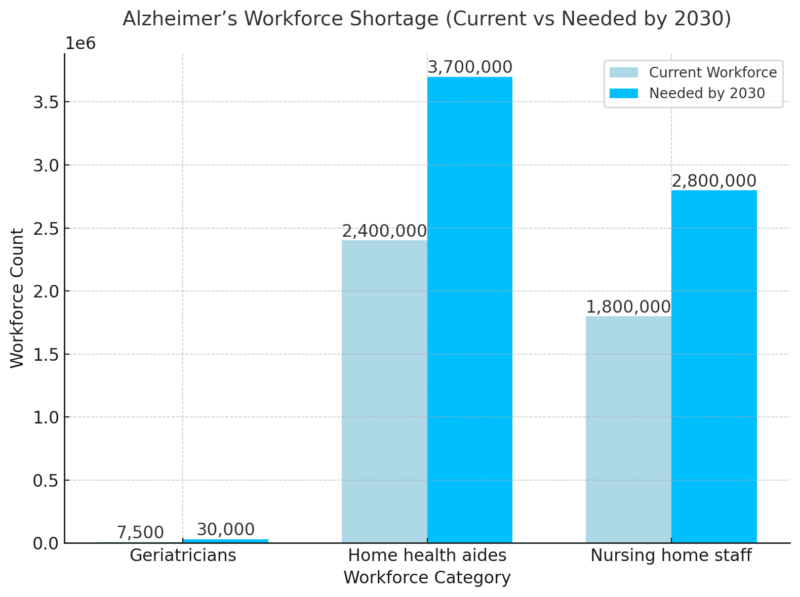
Workforce Challenges and Shortage of Specialists
Alzheimer’s Workforce Shortage
Future Outlook
Current Research Efforts (2025 Update)
Research Focus
Key Findings
Blood tests for early detection
Promising, but not widely available yet
Drug therapies
New FDA-approved drugs slow disease progression
Genetic research
APOE4 gene increases risk significantly
Methodology
References
Related Posts:
- Colorado Population 2025 - Key Facts and Figures
- Scientists Find a Hidden Nutrient Link Between…
- Philadelphia Population 2025 - Current Figures and Analysis
- 10 Shocking Statistics About Heart Disease in 2025
- 10 Statistics About Chronic Disease in Seniors You…
- Is Mallorca Safe to Travel To 2025? Facts About…