Analysts estimate that up to 95 percent of customer interactions could be handled by AI by 2025, and around 80 percent of companies already use or plan to deploy chatbots, according to Master Of Code.
These systems now handle routine questions at scale, operate without downtime, and reduce queues that once defined customer service.
At the same time, the shift is not without trade-offs. While modern large-language-model chatbots can respond in natural language, retain context across sessions, and assist human agents, they also introduce new limitations around accuracy, escalation, and trust.
Table of Contents
ToggleThe Chatbot Revolution: What’s Improved

Round-The-Clock Availability and Faster Resolution
One of the most tangible improvements chatbots brought to customer support is continuous availability. According to McKinsey customer-support professionals, 36 percent identify round-the-clock coverage as the primary benefit of AI adoption, while 31 percent emphasize time savings from automation of manual tasks.
This shift has fundamentally reduced off-hours wait times and shortened queues that once defined customer service outside standard business hours. For customers, this translates into immediate access rather than delayed callbacks or unanswered tickets.
Speed improvements are equally well-documented. Eighty-four percent of businesses report that AI accelerates issue resolution, and 55 percent measure resolution times that are up to 25 percent faster.
When chatbots are used to assist rather than replace human agents, the gains become even more pronounced. AI-assisted agents resolve issues 47 percent faster and achieve 25 percent higher first-contact resolution, indicating that AI works best as a support layer rather than a standalone channel.
High-volume environments benefit from throughput gains as well. Companies that pair human agents with chatbots can handle 7.7 percent more simultaneous chats while saving an estimated US$4.3 million in staffing costs.
In many operations, up to 60 percent of incoming support tickets are resolved through self-service, removing repetitive questions from agent queues and allowing humans to focus on cases that require judgment or negotiation.
Impact of Chatbots on Speed and Capacity
Metric
Measured improvement
24/7 availability cited as key benefit
36% of support professionals
Faster issue resolution
84% of businesses
Resolution time improvement
Up to 25% faster
AI-assisted agent speed
47% faster
First-contact resolution
25% higher
Simultaneous chats handled
+7.7%
Staffing cost savings
US$4.3 million
Tickets resolved via self-service
Up to 60%
Scalability and Cost Savings
The financial case for chatbots will be solidified by 2026. The global chatbot market, valued at US$7.76 billion in 2024, is projected to reach US$27.29 billion by 2030, growing at a compound annual rate exceeding 23 percent, as noted by Grand View Research.
This growth is driven by deployments that show clear and repeatable returns rather than experimental pilots.
Return on investment figures reflect this maturity. Some chatbot deployments report returns as high as 200 percent, while the average investment generates US$3.50 for every US$1 spent.
On the operational side, 95 percent of organizations using AI report measurable time and cost savings. Automation of simple requests reduces response times by 69 percent and cuts operational costs by approximately 30 percent.
The benefits extend to employee productivity. Seventy-nine percent of customer service specialists say AI and automation are important to their strategy, 78 percent feel automation makes them more efficient, and 71 percent report spending more time on tasks they find engaging or meaningful rather than repetitive.
Scalability and Cost Impact
Metric
Reported outcome
Market size 2024
US$7.76 billion
Projected market size 2030
US$27.29 billion
Annual growth rate
23%+
Maximum reported ROI
Up to 200%
Average ROI
US$3.50 per US$1 invested
Organizations reporting savings
95%
Response time reduction
69%
Operational cost reduction
30%
Personalization and Conversational Memory
Modern chatbots differ fundamentally from earlier rule-based systems because they retain context. Generative AI and memory-rich chatbots can recall previous interactions and adjust responses accordingly.
Sixty-four percent of experts say AI increases personalization, and nearly half of surveyed customers believe AI-powered chatbots offer more personalized experiences than traditional support channels.
Customer expectations make this capability essential rather than optional. Sixty-seven percent of customers expect personalization, and 73 percent of shoppers expect brands to understand their unique needs.
By retaining context and tailoring responses, chatbots meet these expectations at scale, something that human agents alone struggle to maintain across millions of interactions.
Multimodal, Omnichannel Support

Customer communication now spans phone, email, web chat, and social messaging. Chatbots operate across all of these channels, including mobile apps and voice interfaces.
Seventy percent of customers worldwide prefer brands that offer service across multiple channels. However, only 13 percent of businesses successfully carry conversation context between channels, creating friction when customers are forced to repeat themselves.
This is where AI provides structural value. Chatbots maintain shared context across channels and sessions, reducing repetition and improving continuity. Customer expectations also extend beyond text.
Over 76 percent of customers want to send text, images, and video within the same conversation. Modern chatbots support attachments and rich media, making troubleshooting and product guidance more precise and reducing ambiguity.
As customer expectations move beyond text, voice is becoming a critical part of AI-driven support. Real-time text-to-speech systems now allow chatbots and virtual agents to deliver spoken responses instantly, enabling more natural phone-based and voice-assistant interactions.
This is especially relevant for accessibility, hands-free support, and global customer bases where spoken interaction reduces friction. For a technical example of how real-time voice synthesis is implemented in customer-facing AI systems, click here.
Omnichannel and Multimodal Expectations
Metric
Percentage
Customers prefer omnichannel support
70%
Businesses carrying context across channels
13%
Customers want text, images, and video
76%+
Empowering Agents Through AI Assistance
Chatbots increasingly serve as tools for agents rather than replacements. Forty percent of support units have introduced agent-assist features that suggest responses, summarize conversations, and automatically route tickets.
These systems reduce cognitive load and improve consistency across interactions.
The operational impact is measurable. Informatica Organizations report 27 percent reductions in average handle time after introducing agent-assist AI. Collaboration improves as well, with 75 percent of customer service specialists saying AI enhances collaboration and data sharing.
Embedded AI tools inside CRM platforms allow agents to retrieve knowledge and recommendations instantly instead of navigating fragmented systems.
Data-Driven Insights and Predictive Analytics
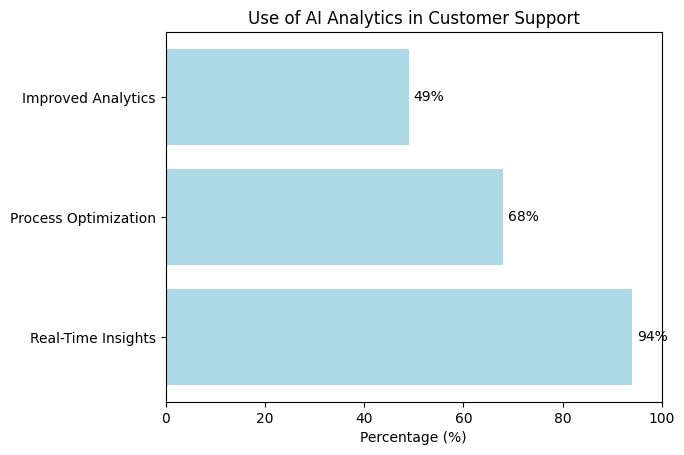
Beyond direct interaction, chatbots generate data at scale. Ninety-four percent of service leaders consider real-time insights and reporting critical. AI analyzes conversation trends, sentiment shifts, and churn signals, enabling proactive outreach rather than reactive support.
Executives report using AI for process optimization in 68 percent of cases and for improved analytics in 49 percent. Predictive models identify customers at risk of defection or suitable for upsell opportunities, turning customer support from a cost center into a strategic function.
Use of AI Analytics in Customer Support
Where Chatbots Still Fall Short
Despite clear gains in speed and scale, chatbots introduce new weaknesses that remain unresolved in 2026. The biggest problems emerge when interactions move beyond simple, well-defined tasks.
Complexity, Escalation, and User Frustration
Chatbots still struggle with complex and ambiguous issues. A Bain & Co. study shows that digital channels score 31–53 points on complex questions, compared to 44–63 for human agents. When answers fall short, customers often demand a human.
This friction shows up clearly in behavior: 45 percent of users abandon chatbot conversations after three failed attempts, and more than 65 percent of abandonment is caused by poor escalation design.
Repetition remains a major pain point. A 2025 U.S. survey found that 90 percent of customers had to repeat information to chatbots within the past year. RAG-based bots resolve only 10–20 percent of tickets, and despite 70 percent of CX leaders adopting AI, just 17 percent of consumers felt wait times actually improved.
Hallucinations and Reliability Risks

Accuracy is another persistent weakness. Forty percent of support teams cite occasional inaccuracies as a barrier, and 55 percent worry chatbots provide incorrect information. Only 42 percent feel confident detecting hallucinated answers. As a result, organizations invest heavily in safeguards.
Financial institutions like ING restrict AI from giving mortgage or investment advice, and low-confidence outputs trigger immediate human takeover. Leaders note that 95 percent of the work lies not in the model itself, but in the surrounding control systems.
Empathy Gaps and Emotional Limitations
While chatbots communicate fluently, they still lack emotional depth. Thirty-six percent of consumers say AI chat feels less personal, and 44 percent prefer human agents.
Although 67 percent believe bots could eventually form stronger emotional connections, current systems struggle to interpret frustration, sarcasm, or emotional context. When customers feel misunderstood, trust erodes quickly, and churn risk increases.
Integration, Cost, and Data Challenges
AI performance is limited by data access. Thirty-two percent of teams struggle to integrate chatbots with existing systems, and fragmented knowledge bases often lead to incorrect answers.
Implementation costs vary widely, from US$5,000 to US$500,000, depending on complexity. While ROI can be high, organizations without clean data, defined workflows, or clear ownership often fail to see meaningful returns.
Trust, Ethics, and Regulatory Pressure
Trust remains fragile. Sixty-three percent of consumers worry about bias or discrimination from AI, and only 20 percent are fully comfortable with chatbot use, rating AI support 3 out of 5.
Transparency matters: over 90 percent of businesses and consumers believe companies should disclose AI usage, and 77 percent favor human monitoring.
Parliament approved the Artificial Intelligence Act which aims to make the EU a world leader in safe and trustworthy AI.
These rules are some of the first in the world to protect people from high-risk AI while encouraging innovation.
Find out more: https://t.co/zUkjfl4HvO pic.twitter.com/Ukz8sWalLE
— European Parliament (@Europarl_EN) April 13, 2024
Regulation reinforces this pressure. The EU AI Act, enforced in 2024, mandates documentation, risk assessment, and monitoring for high-risk systems. In the U.S., the FTC’s Operation AI Comply signals that deceptive AI practices can lead to enforcement action.
Internally, 39 percent of support teams worry AI will replace their jobs, slowing adoption and cooperation.
Over-Reliance and Brand Risk
Customers expect instant human fallback when bots fail. Poor escalation damages trust and brand perception. Klarna’s experience is a clear warning: after claiming its AI assistant could replace 700 support staff, customer satisfaction declined, forcing the company to rehire human agents.
Chatbot errors spread quickly on social media, and customers rarely separate the bot’s mistake from the brand itself.
Case Studies: What Works and What Breaks
Verizon used AI to assist agents rather than replace them. Its generative AI tools draw from 15,000 internal documents, helping agents answer 95 percent of queries and contributing to a 40 percent increase in sales, as agents spent less time searching for information and more time selling.
ING handles 85,000 service queries per week. After rolling out conversational AI to 10 percent of customers, it served 20 percent more users within seven weeks while improving satisfaction. Crucially, ING restricts AI from giving financial advice and escalates low-confidence answers to humans.
United Airlines combined AI with human oversight in its “Every Flight Has a Story” initiative. AI-generated explanations for delays increased customer satisfaction by 6 percent, while human reviewers ensured tone and accuracy.
Klarna illustrates the downside of over-automation, while a Slovak micro-enterprise study shows the middle ground: AI reduced workload and improved response speed, but struggled with ambiguity and empathy, requiring continuous human oversight.
Trends and the Road Ahead

Analysts predict 85 percent of customer service interactions could be handled without a human agent, and 80 percent of organizations plan to deploy generative AI. Eighty-three percent expect to increase AI investment, with the fastest adoption in retail, telecom, and banking.
The next phase focuses on agentic AI capable of reasoning and taking action, but regulation and ethics are shaping deployment. Sixty-nine percent of CX leaders now have ethical AI plans, and 74 percent emphasize transparency and data security.
Gartner estimates conversational AI could cut contact-center labor costs by US$80 billion by 2026, but only if systems are governed carefully.
What This Means for Brands
Strengths
Weaknesses
Practical response
24/7 availability
Poor handling of complex or emotional issues
Design seamless human escalation
Scalability and cost savings
Hallucinations and inaccuracies
Add guardrails and monitoring
Personalization and memory
Limited empathy
Reserve humans for high-empathy cases
Agent productivity
Data and integration gaps
Invest in data quality and governance
Multichannel support
Trust and regulatory risk
Be transparent and maintain oversight
Conclusion
By 2026, chatbots are essential part of the infrastructure in customer support. They deliver speed, scale, and cost efficiency, and they clearly boost productivity and revenue when used correctly.
But they still fail where judgment, empathy, and trust matter most. The strongest results come from hybrid models that pair AI efficiency with human oversight, robust data governance, and clear ethical boundaries.