Healthcare is a field that has experienced a lot of advancements that push medical care closer to:
Technology such as artificial intelligence, robotics, and portable diagnostics has moved from experimental concepts into real-world clinical applications.
These shifts are changing not only how diseases are diagnosed but also how care is delivered in:
Today, we will touch upon the top ten latest breakthroughs in medical and testing equipment.
No.
Breakthrough
Description
Key Benefits
1
Portable Ultra-Low-Field MRI
Bedside MRI with AI imaging.
Faster stroke checks, safe, mobile.
2
AI-Enhanced Portable Cardiac Ultrasound
Portable ultrasound with AI guidance.
Quick scans, early detection, rural use.
3
AI-Powered Diagnostic Imaging Systems
AI for CT, cancer, and skin analysis.
Faster, more accurate diagnoses.
4
Wearable Diagnostic Devices
Smartwatches, sweat, and glucose trackers.
Early alerts, continuous monitoring.
5
AI Genetic Risk Prediction Tools
AI predicts hereditary disease risks.
Targeted screening, prevention.
6
Digital Twin Technology
Virtual patient/surgery models.
Safer planning, personalized care.
7
AI Administrative Copilots
AI automates medical paperwork.
Saves time, fewer errors.
8
3D-Printed Medical Solutions
Custom implants, drugs, models.
Better fit, safer surgeries.
9
CRISPR & Gene Editing Tools
Gene therapies and diagnostics.
Curative treatments, fast testing.
10
Conversational AI in Healthcare
Chatbots and robots for care support.
Mental health aid, remote access.
Table of Contents
Toggle1. Portable Ultra-Low-Field MRI
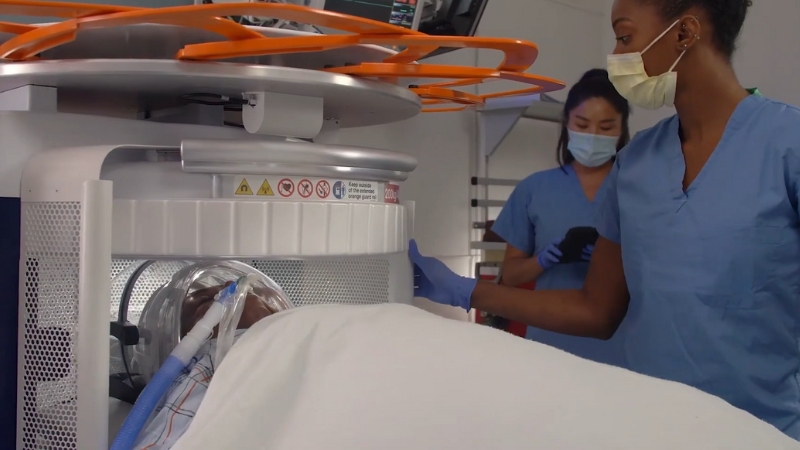
Portable MRI technology in 2025 has matured to the point where clinicians can perform full diagnostic imaging right at the patient’s bedside.
The first FDA 510(k) clearance for a bedside portable brain MRI (Hyperfine Swoop) came in February 2020; a deep-learning image reconstruction upgrade was cleared in Nov 2021; and a next-generation Swoop with Optive AI and a redesigned, lighter scanner received FDA clearance on June 2, 2025.
Early bedside feasibility and safety were demonstrated in ICUs at Yale New Haven Hospital and Massachusetts General Hospital.
Hyperfine also announced the first commercial sales of the new 2025 system to leading U.S. hospitals.
Bedside brain imaging avoids transport delays, enables ICU/ED stroke and trauma evaluations, and, per emerging data, can markedly speed stroke imaging workflows in emergency departments.
RSNA coverage and trade analyses highlight access gains for stroke triage.
Key features include (unchanged, now evidence-tied):
- Compact design for ICUs/ERs/rural clinics
- Radiation-free scans
- Rapid deployment
2. AI-Enhanced Portable Cardiac Ultrasound
Portable ultrasound devices now provide advanced cardiac evaluations powered by AI.
Esaote’s MyLab C30 Cardio launched in 2025 (previewed at ECR in Feb 2025 and showcased at ESC 2025 in August), adding AI tools such as HeartScan Assistant for guidance and quality optimization.
Vendor announcements position C30 for cardiology across hospitals and ambulances; more broadly, AI-guided POCUS is being adopted across health systems (e.g., GE HealthCare’s AI-guided Venue family) and studied for rural networks.
Real-time AI assistance improves view acquisition, cuts exam time, and helps non-specialists capture diagnostic-quality images—particularly valuable in ambulances and rural settings.
Highlighted advantages:
- Real-time AI assistance: Optimizes image quality instantly.
- Expanded access: Cardiac diagnostics in ambulances and field settings.
- Life-saving efficiency: Earlier intervention during heart attacks.
- Resource flexibility: Supports hospitals lacking specialized staff.
3. AI-Powered Diagnostic Imaging Systems
AI has accelerated the speed and accuracy of imaging across multiple fields.
By late 2024–2025, all 107 stroke centres in England had AI tools (e.g., Brainomix 360, RapidAI) deployed for near-instant CT analysis; national programs funded roll-out so decisions happen faster, with recent reports citing sharply improved door-to-treatment times and functional outcomes.
Examples include Royal Berkshire (Brainomix study sites) and Russells Hall Hospital, Dudley (RapidAI).
Large real-world evaluations (80k+ pts) linked stroke AI to more thrombectomies and improved access; government summaries describe real-time decision support across NHS networks.
Transpara AI is used in European/UK screening programs and studies show workload reduction and detection gains when used with radiologists; an ongoing mega-trial in the NHS (≈700k mammograms) launched in Feb 2025.
Skin Analytics’ DERM received conditional NHS use (NICE) in 2025 and is being rolled out across additional trusts to triage lesions within minutes and cut waits.
Applications include:
- Stroke detection: AI-powered brain scans in emergency care.
- Cancer screening: Breast cancer detection outperforms traditional methods.
- Dermatology: Automated analysis of skin lesions in primary care.
- Efficiency gains: Lower costs and reduced diagnostic delays.
4. Wearable Diagnostic Devices with Clinical Accuracy

Wearables now reach clinical-grade use in targeted areas.
Apple Watch’s ECG app and irregular rhythm notification features received regulatory clearance (2018 US; CE mark in EU/UK soon after) and have clinical-study support for AFib detection. Hospitals use streams of such data in cardiology follow-ups.
The Gatorade/Epicore Gx Sweat Patch and Nix Biosensors provide real-time sweat electrolyte and fluid-loss insights; validation and post-market studies describe personalized hydration guidance (helpful for athletes and heat-exposed patients).
High-profile efforts (e.g., Verily) were halted in 2018 due to biological/technical constraints; this remains experimental, not a clinical standard.
These devices feed data to clinicians for proactive interventions and reduced visits where appropriate.
Examples include:
- ECG-enabled smartwatches: Early arrhythmia detection.
- Glucose-monitoring contact lenses: Non-invasive diabetes management.
- Hydration trackers: Monitoring electrolyte balance.
- IoMT integration: Real-time communication with healthcare providers.
5. AI-Based Genetic Risk Prediction Tools
AI has advanced genetic prediction by analyzing millions of patient records, offering risk assessment for over 1,600 hereditary diseases.
In September 2025, researchers unveiled Delphi-2M, an AI model forecasting risk for 1,000+ diseases years in advance using large EHR cohorts (UK Biobank & Danish registries). While promising, it’s not yet routine clinical practice.
Doctors now use these predictions to recommend tailored screening for conditions such as breast cancer and kidney disease.
Early identification empowers patients to adopt preventive measures long before symptoms occur.
The UK is exploring polygenic risk scores within a Genomics Population Health Service, but leading bioethics groups advise a cautious, targeted roll-out of AI-powered genomic prediction.
Better targeting of screening (e.g., breast/renal risk), earlier preventive steps, and more efficient use of resources—pending further validation and governance.
Practical uses:
- Risk prediction: Analysis of hereditary conditions at scale.
- Targeted screening: Focused on higher-risk patients.
- Patient empowerment: Preventive lifestyle adjustments.
- Healthcare efficiency: Optimized use of diagnostic resources.
6. Digital Twin Technology for Predictive Treatment
A decade after the first virtual heart twin, Dassault Systèmes’ Living Heart Project advanced to next-gen parametric models in 2025, after a multi-year FDA collaboration.
Digital twin models replicate patients virtually, enabling healthcare providers to test treatments or surgical procedures before they occur in reality.
Surgeons rely on digital twins to reduce risks during complex operations, while pharmaceutical researchers test drugs on virtual patient groups.
Hospital administrators simulate different operational workflows to improve patient throughput and optimize staffing.
Personalized planning ensures higher precision in treatment, reduced errors, and faster innovation in clinical research.
Safer surgical planning, device testing in silico, and hospital-operations twins for throughput/staffing optimization (e.g., GE HealthCare Command Center Digital Twin; peer-reviewed ops research).
Core applications:
- Surgical planning: Reduced risk and improved outcomes.
- Drug discovery: Simulated testing on virtual patient groups.
- Hospital management: Modeling patient flow and resources.
- Patient-specific care: Customized treatment strategies.
7. AI-Powered Administrative Copilots
Nuance/Microsoft’s Dragon Ambient eXperience (DAX) Copilot became generally available and embedded in Epic by Jan 2024; 150+ health systems are deploying it.
Microsoft consolidated its offerings as Dragon Copilot in 2025.
The most important benefits of AI-powered administrative copilots are: automated note-taking and discharge letters save clinician hours, reduce documentation errors, shorten discharge delays, and improve throughput—freeing staff for patient care.
Key functions:
- Automated paperwork: Faster discharge and record-keeping.
- Error reduction: Accurate medical documentation.
- Clinician focus: More time for patient care.
- Hospital efficiency: Improved throughput and compliance.
8. 3D-Printed Personalized Medical Solutions

Clinical 3D printing has been present for a decade, but point-of-care labs and pediatric dosing pilots accelerated 2024–2025 (e.g., ECR 2025 launch of Esaote’s new portable line is separate; in 3D meds, UCL/Vall d’Hebron & St. Jude projects).
Hospitals that use this tech are:
Prosthetics and implants can now be customized to match individual patients perfectly, improving comfort and functionality.
Pediatric medications are produced in personalized dosages to enhance treatment adherence.
Surgeons use 3D-printed models to prepare for complex operations, reducing risks and shortening surgery times.
Bioprinting has moved into the early stages of functional tissue development, offering a preview of future organ transplantation possibilities.
Personalized solutions reduce waste, cut costs, and raise treatment success rates.
Highlights include:
- Customized prosthetics and implants: Tailored for comfort and performance.
- Personalized pediatric drugs: Accurate dosing for children.
- Surgical preparation models: Patient-specific training tools.
- Bioprinting: Early-stage tissue and organ prototypes.
9. CRISPR & Next-Gen Gene Editing Tools
Gene editing with CRISPR has entered mainstream medicine with approved therapies treating rare genetic disorders such as beta-thalassemia.
Patients once limited to symptomatic treatments now receive curative interventions at the genetic level.
Compact CRISPR-based diagnostic devices are being tested in clinics, offering rapid detection of genetic mutations directly at the point of care.
Such innovations bring genetic testing into remote and underserved areas, making early diagnosis more accessible.
Precision targeting of mutations marks a significant shift toward treating diseases at their origin rather than just managing symptoms.
Breakthrough aspects:
- Clinical therapies: Approved CRISPR treatments for rare diseases.
- Point-of-care diagnostics: Compact CRISPR testing devices.
- Rapid mutation detection: Results within minutes.
- Improved accessibility: Expanding genetic testing in underserved regions.
10. Conversational AI & AI Copilots in Remote & Mental Healthcare
@abc7nySome people are turning to AI chatbots for therapy. A mental health expert weighs in on the applications and limitations of Artificial Intelligence.♬ original sound – ABC7NY
NHS services have been piloting AI mental-health chatbots (e.g., Wysa) with RCTs and Talking Therapies integrations; meanwhile, ElliQ companion robots showed a 95% reduction in loneliness in New York State’s program (results published 2023, continuing adoption noted in 2024–2025).
Where in practice:
Reproductive health chatbots are under active development and evaluation to deliver private, evidence-based guidance.
Expanded access, privacy-preserving support, improved adherence (reminders), and reduced loneliness, while clinicians remain in the loop for diagnosis/therapy.
Chatbots now deliver trusted reproductive health guidance, while AI mental health coaches support individuals struggling with stress and anxiety.
Increased accessibility leads to improved treatment adherence and stronger patient engagement.
Examples of impact:
- Reproductive health support: Confidential chatbot assistance.
- Mental health coaching: Continuous stress management tools.
- Elderly care companions: Social interaction and reminders.
- Rural access: Breaking barriers of distance and stigma.
Summary
Medical and diagnostic breakthroughs in 2025 are reshaping how healthcare is:
- Delivered
- Diagnosed
- Managed
AI, portability, and personalization are driving forces behind this transformation, ensuring care reaches more people with greater accuracy.
Hospitals, clinics, and homes are becoming interconnected through advanced equipment and smart systems that optimize both prevention and treatment.
Stakeholders now face the responsibility of adopting these technologies while ensuring equitable access, ethical use, and robust regulation.