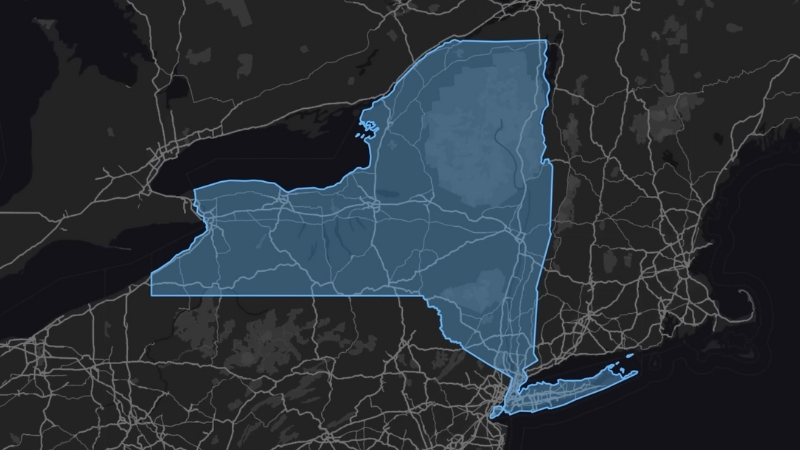
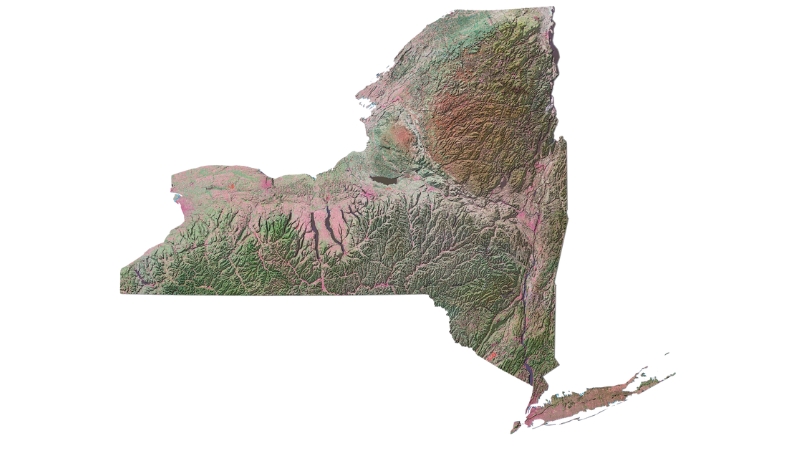
New York State is located in the northeastern United States, bordered by the Canadian provinces of Québec and Ontario to the north, Lake Ontario to the northwest, and the Atlantic Ocean to the southeast.
It shares borders with the U.S. states of Vermont, Massachusetts, Connecticut, New Jersey, and Pennsylvania.
Part of the state’s northern boundary with Canada is defined by the St. Lawrence River.
As of 2025, New York State’s population stands at 19.57 million, with New York City alone accounting for approximately 8,097,282 residents.
Originally settled by the Dutch, the region was handed over to the British in 1664. New York was part of the original territory of the United States, and its charter in 1664 included a larger area.
Portions of this territory were later ceded to form New Jersey, Delaware, and Pennsylvania. New York ratified the U.S. Constitution on July 26, 1788, becoming the 11th of the original 13 states to join the Union.
| Aspect | Facts |
|---|---|
| Also Known As | Empire State |
| State Nickname | Empire State |
| State Motto | “Excelsior” (Ever Upward) |
| State Bird | Eastern Bluebird |
| State Flower | Rose |
| State Song | “I Love New York” |
| Capital | Albany |
| Population | 19.57 million |
| Largest City and County | New York City, Kings County (Brooklyn) |
| Date of Admission | July 26, 1788 |
| State Size | 54,555 square miles (141,297 km²) |
| Geographic Features | Adirondack and Catskill Mountains; Hudson and Niagara Rivers |
| Borders | Canada, Vermont, Massachusetts, Connecticut, New Jersey, Pennsylvania; Atlantic Ocean |
| Climate | Humid continental; humid subtropical in NYC area |
| Area (Water) | 7,429 sq mi (19,226 km²), 13.6% of the total |
| Notable Sites | Statue of Liberty, Niagara Falls, Empire State Building |
| Electoral Votes | 29 |
| Time Zone | Eastern (GMT − 5 hours) |
Table of Contents
ToggleNew York State Map and Satelite View
NY is one of the original 13 colonies and the fourth-most populous state as of 2025, with a population of nearly 19.6 million.
The state’s geography is diverse, with urban centers like New York City in the southeast, the Adirondack and Catskill mountains upstate, and the Great Lakes region in the west.
New York was originally settled by the Dutch in 1621 as New Netherland, later seized by the English in 1664, and eventually became a major center of trade and industry following the construction of the Erie Canal in the early 19th century.
The state has a significant history of immigration, particularly through Ellis Island, which saw millions of immigrants enter the U.S. during the 19th and early 20th centuries.
New York played a central role in both the Revolutionary War and the Civil War, and today, New York City remains a global financial, cultural, and media hub.
Recent events, such as the September 11 attacks, Hurricane Sandy, and the COVID-19 pandemic, have significantly impacted the state, leading to substantial rebuilding efforts and new public health policies.
Known for its economic, cultural, and historical significance, with landmark attractions like Times Square, Niagara Falls, and the Statue of Liberty drawing millions of visitors annually.
Geography Map
-
Source: gisgeography.com, New York is the 27th-largest state in the U.S.
Located in the northeastern United States, bordered by five states—Connecticut, Massachusetts, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and Vermont—as well as Canada and two Great Lakes, Erie and Ontario.
Covering an area of 54,555 square miles, New York is the 27th-largest state in the U.S. Its highest point is Mount Marcy in the Adirondacks, at 5,344 feet, while its lowest is at sea level along the Atlantic Ocean in Downstate New York.
The state features a variety of landscapes, with urban areas like New York City contrasting with expansive forests, rivers, farms, and mountain ranges.
The Allegheny Plateau runs across the southern part of the state, while the Adirondack and Catskill Mountains occupy significant portions of the north and east, respectively.
New York is often divided into Upstate and Downstate regions, although these terms are unofficial and have loose boundaries.
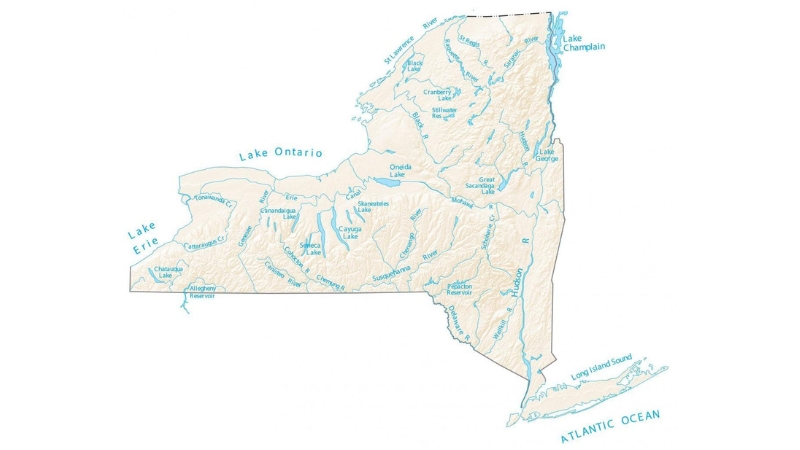
Water and Borders
- Source: gisgeography.com, Approximately 13.6% of New York’s total area is water
New York is defined by significant water borders, including the Atlantic Ocean and Long Island Sound to the southeast.
This coastal region includes New York City and Long Island, home to over 11 million residents—more than half the state’s population.
Roughly 13.6% of New York’s area consists of water, with borders formed by the Great Lakes, the Niagara River, and the St. Lawrence River.
Additional water boundaries include Lake Champlain along the Vermont border, and various rivers and bodies of water along the borders with New Jersey and Pennsylvania.
Unique among U.S. states, New York has access to both the Great Lakes and the Atlantic Ocean, contributing to its role as a major commercial hub.
Drainage Systems
The Hudson River, originating near Lake Tear of the Clouds, flows south through the eastern state, while Lake Champlain drains into Canada via the Richelieu River and then into the Saint Lawrence River.
Western New York is primarily drained by the Allegheny River and the Susquehanna and Delaware River systems.
The iconic Niagara Falls, located on the Niagara River, connects Lake Erie to Lake Ontario and is shared between New York and Ontario, Canada.
The Delaware River Basin Compact, agreed upon in 1961, regulates water use in the Delaware system among New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Delaware, and the federal government.
Climate
Temperatures soared to well above normal readings earlier today. Temperatures stay above normal into Friday, but a noticeable cool down begins later Friday and into the weekend. #nycwx #hvwx #liwx #njwx #ctwx #nywx pic.twitter.com/bFwmaYPJ9p
— NWS New York NY (@NWSNewYorkNY) November 7, 2024
Most of the state experiences a humid continental climate, while New York City and Long Island have a humid subtropical climate.
Downstate New York, which includes New York City, has hot, humid summers and relatively mild winters due to its lower elevation and proximity to the Atlantic Ocean.
Upstate New York has long, cold winters, particularly in areas like the Tug Hill Plateau, which experiences heavy lake-effect snow.
Summers are mild to warm in Upstate regions, while mountainous areas like the Adirondacks remain cool.
Temperature extremes have ranged from a high of 108°F in 1926 to a low of -52°F in 1979, illustrating the state’s climate variability.
Flora and Fauna
Forest types range from Southern Great Lakes forests in Western New York to Atlantic coastal pine barrens in Long Island.
Wildlife includes mammals such as white-tailed deer, black bears, and bobcats, as well as extirpated species like the eastern cougar.
Bird species, including the blue jay, eastern bluebird (state bird), and bald eagle, are common, while several types of reptiles, amphibians, and marine species inhabit the state’s diverse environments.
The Hudson River and New York Harbor support an estuary ecosystem, home to various fish, shellfish, and shorebirds.
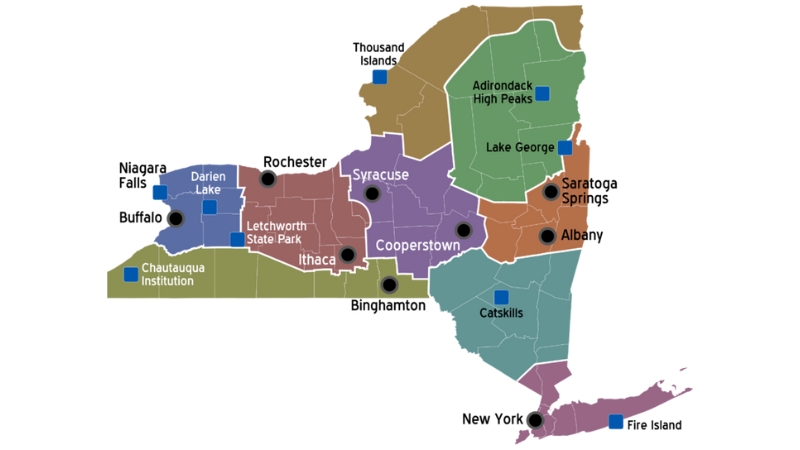
Economic and Tourism Regions
- Source: en.wikivoyage.org, These divisions fuel regional growth
Divided into ten economic regions for administrative purposes, including Western New York, the Finger Lakes, the Southern Tier, Central New York, and the Capital District.
These economic divisions support the state’s wide-ranging industries and regional growth.
The state is also divided into eleven tourism regions, such as the Adirondack Mountains, Catskill Mountains, and Long Island, which highlight New York’s natural and cultural attractions.
From the urban appeal of New York City to the natural beauty of regions like the Thousand Islands, New York offers varied tourism experiences for visitors.
State Parks and National Landmarks
Niagara Falls State Park, established in 1885, is the oldest in the nation, while the vast Adirondack Park, created in 1892, is the largest state park in the U.S. and is protected as “forever wild.”
The Catskill Park, with 700,000 acres of preserved land, provides a habitat for diverse wildlife. Major tourist attractions include the Statue of Liberty, a symbol of democracy, and the African Burial Ground National Monument, dedicated to the legacy of enslaved Africans.
Fire Island, General Grant National Memorial, and Saratoga National Historical Park are among the state’s other historic and recreational landmarks.
Natural Wonders
The Adirondack Mountains, located in the northeastern part of the state, feature some of the most popular destinations like Mirror Lake, Tupper Lake, and The Wild Center in Adirondack Park.
A recent addition to the area’s attractions is the Wild Walk, a series of elevated bridges allowing visitors to explore the treetops. Mount Marcy, the highest point in New York at 1,628 meters (5,344 feet), is situated in the Adirondacks near Lake Placid.
November mist 💧 pic.twitter.com/liqNAXArx0
— Niagara Falls USA (@NiagaraFallsUSA) November 7, 2024
Another world-famous natural landmark is Niagara Falls, where the American Falls and Bridal Veil Falls cascade on the U.S. side, adjacent to the Horseshoe Falls on the Canadian border.
To the southwest, the vast Allegheny Plateau, part of the Appalachian Highlands, encompasses the Catskill Mountains, which are known for hiking trails, rich wildlife, and winter resorts, making it a popular year-round destination.
Administrative Divisions
| County | FIPS Code |
|---|---|
| Albany | 001 |
| Allegany | 003 |
| Bronx | 005 |
| Broome | 007 |
| Cattaraugus | 009 |
| Cayuga | 011 |
| Chautauqua | 013 |
| Chemung | 015 |
| Chenango | 017 |
| Clinton | 019 |
| Columbia | 021 |
| Cortland | 023 |
| Delaware | 025 |
| Dutchess | 027 |
| Erie | 029 |
| Essex | 031 |
| Franklin | 033 |
| Fulton | 035 |
| Genesee | 037 |
| Greene | 039 |
| Hamilton | 041 |
| Herkimer | 043 |
| Jefferson | 045 |
| Kings | 047 |
| Lewis | 049 |
| Livingston | 051 |
| Madison | 053 |
| Monroe | 055 |
| Montgomery | 057 |
| Nassau | 059 |
| New York | 061 |
| Niagara | 063 |
| Oneida | 065 |
| Onondaga | 067 |
| Ontario | 069 |
| Orange | 071 |
| Orleans | 073 |
| Oswego | 075 |
| Otsego | 077 |
| Putnam | 079 |
| Queens | 081 |
| Rensselaer | 083 |
| Richmond | 085 |
| Rockland | 087 |
| St. Lawrence | 089 |
| Saratoga | 091 |
| Schenectady | 093 |
| Schoharie | 095 |
| Schuyler | 097 |
| Seneca | 099 |
| Steuben | 101 |
| Suffolk | 103 |
| Sullivan | 105 |
| Tioga | 107 |
| Tompkins | 109 |
| Ulster | 111 |
| Warren | 113 |
| Washington | 115 |
| Wayne | 117 |
| Westchester | 119 |
| Wyoming | 121 |
| Yates | 123 |
The State is divided into 62 counties, with each county (except the five counties of New York City) further subdivided into towns and cities according to government sources.
New York City itself is divided into five boroughs, each corresponding to a county. Other significant urban areas include Buffalo, Rochester, and the Capital District cities of Albany, Schenectady, and Troy.
The state’s urban areas developed along key trade and transportation routes, including the Erie Canal.
Today, the New York Thruway and various railroads continue to facilitate movement across the state, linking it to the broader Northeast megalopolis.
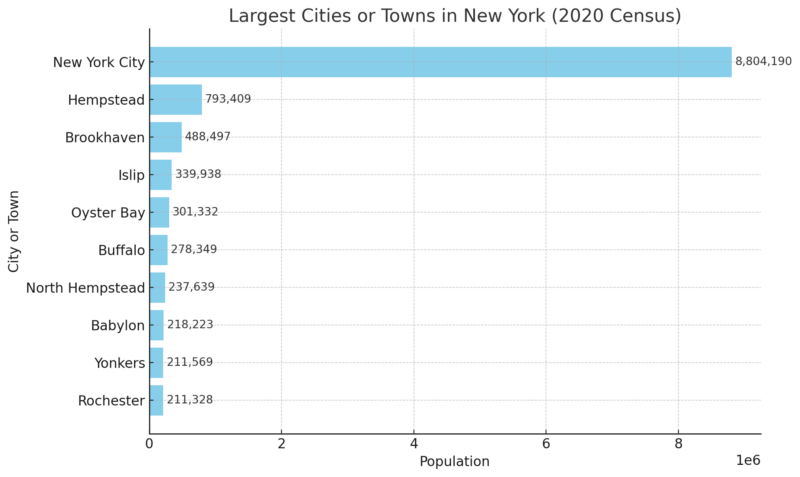
Largest Cities or Towns in New York (2020 Census)
- Largest cities or towns in New York chart
| City or Town | Population |
|---|---|
| New York City | 8,804,190 |
| Hempstead | 793,409 |
| Brookhaven | 488,497 |
| Islip | 339,938 |
| Oyster Bay | 301,332 |
| Buffalo | 278,349 |
| North Hempstead | 237,639 |
| Babylon | 218,223 |
| Yonkers | 211,569 |
| Rochester | 211,328 |
New York State’s largest cities and towns reflect a mix of dense urban hubs, sprawling suburban communities, and historic industrial centers.
New York City, with a population of over 8.8 million, is by far the largest and stands as a global financial, cultural, and media powerhouse.
Long Island towns like Hempstead, Brookhaven, and Islip follow in size, supporting substantial suburban populations with strong connections to NYC.
Upstate cities like Buffalo and Rochester add diversity, each with a rich industrial heritage and ongoing revitalization in sectors like healthcare, technology, and education.
Population Heat Map
It is the fourth-most populous U.S. state, with an estimated population of around 19.6 million according to World Population Review.
The New York metropolitan area, which includes New York City and Long Island, houses over half of the state’s population.
This region, along with the Capital District and Buffalo-Niagara metropolitan area, has experienced growth, while other areas, such as Rochester and Syracuse, have faced population decline.
The state capital, Albany, along with these major cities, highlights regional population shifts, with growth primarily in the metropolitan areas and population declines in some upstate regions, while New York continues to attract a diverse international population.
The state is highly urbanized, with 92% of residents living in urban areas, largely concentrated in New York City.
Despite recent population losses, particularly after 2020, the state remains a major destination for international immigrants, hosting one of the most diverse populations in the country.
| Census Year | Population | % Change |
|---|---|---|
| 1790 | 340,120 | — |
| 1900 | 7,268,894 | 21.1% |
| 1950 | 14,830,192 | 10.0% |
| 2000 | 18,976,457 | 5.5% |
| 2020 | 20,201,249 | 4.2% |
| 2023 (est.) | 19,571,216 | -3.1% |
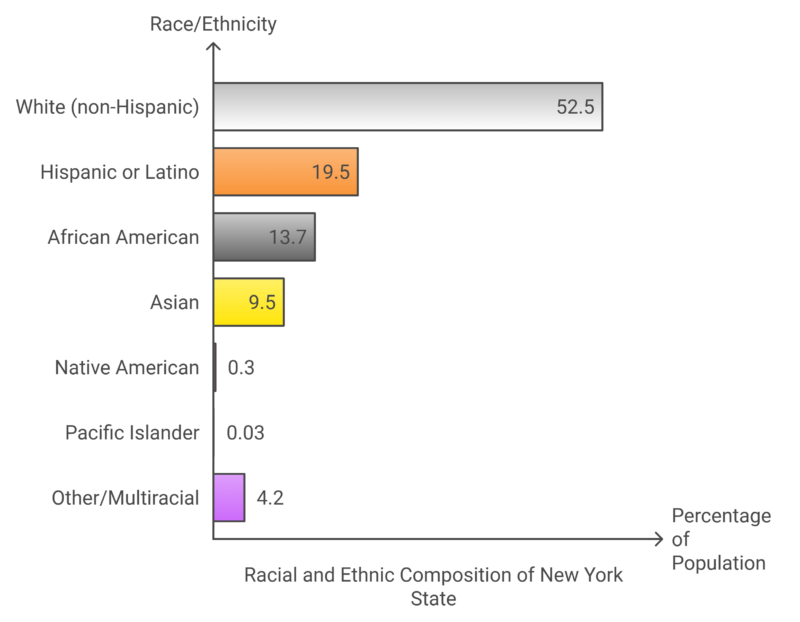
Race and Ethnicity
- Racial and ethnic composition of New York State chart
According to the 2020 Census, non-Hispanic White people made up 52.5% of the state’s population, while Hispanic or Latino people accounted for 19.5%, and African Americans for 13.7%.
New York has large Asian and Jewish populations, with Queens being the most ethnically diverse county in the United States.
The state also has significant Hispanic, African American, and Caribbean communities, with large numbers of Puerto Ricans, Dominicans, and Jamaican Americans. New York’s diversity is further underscored by its role as a leading state for new immigrants from around the world.
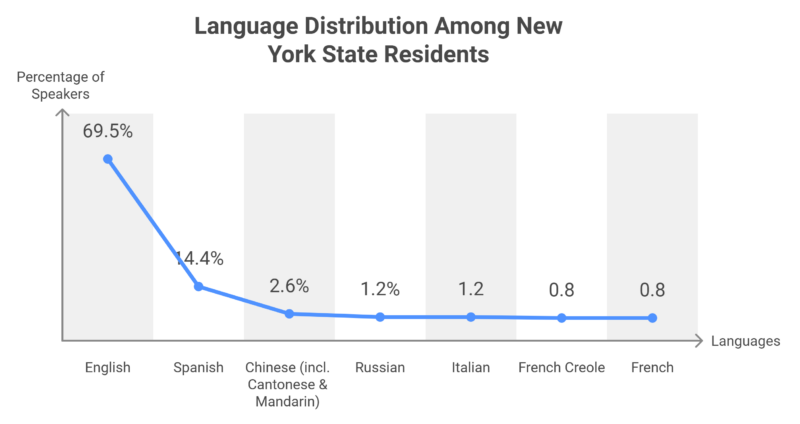
Languages
- New York City hosts around 800 spoken languages
Linguistically diverse, with nearly 30% of residents speaking a language other than English at home.
Spanish is the most commonly spoken non-English language, followed by Chinese, Russian, and Italian.
New York City alone is estimated to have up to 800 languages spoken, making it one of the most linguistically diverse cities globally. In total, nearly six million New Yorkers speak a language other than English at home.
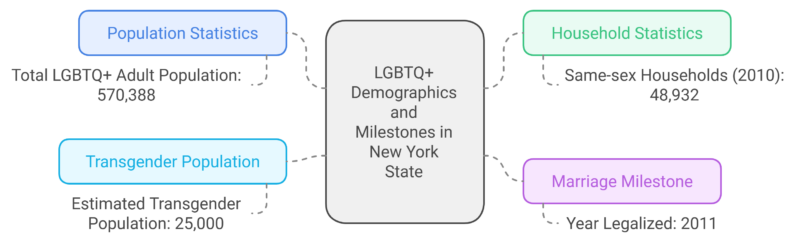
Sexual Orientation and Gender Identity
- Same-sex marriage became legal in New York in 2011
Approximately 3.8% of New York’s adult population identifies as LGBTQ+, with New York City recognized as a major center for LGBTQ culture and activism.
The Stonewall Inn in Greenwich Village was the site of the 1969 Stonewall riots, a pivotal event in the LGBTQ rights movement.
The state legalized same-sex marriage in 2011, and New York City hosts one of the largest pride parades in the world.
In 2019, the city commemorated the 50th anniversary of the Stonewall riots with a record-breaking WorldPride event.
Immigration and Ancestry
The top countries of origin include the Dominican Republic, China, and India.
The city’s neighborhoods have diverse cultural representations, with areas like Queens hosting large Andean, Chinese, and Caribbean communities.
Italian, Irish, German, and French ancestries are common throughout the state, with Italian Americans prominent on Staten Island and Long Island, and French Canadian heritage prevalent in the North Country.
Airports In New York
| Airport Name | IATA Code | ICAO Code | Passenger Capacity (Annual) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Albany International Airport | ALB | KALB | 1,440,674 |
| Greater Binghamton Airport | BGM | KBGM | 36,382 |
| Buffalo Niagara International Airport | BUF | KBUF | 2,523,158 |
| Westchester County Airport | HPN | KHPN | 789,283 |
| Long Island MacArthur Airport | ISP | KISP | 811,535 |
| John F. Kennedy International Airport | JFK | KJFK | 30,620,769 |
| Jamestown Airport | JHW | KJHW | 92 |
| Downtown Manhattan Heliport | JRB | KJRB | 51 |
| LaGuardia Airport | LGA | KLGA | 15,058,501 |
| Massena International Airport | MSS | KMSS | 4,463 |
| Ogdensburg International Airport | OGS | KOGS | 23,448 |
| Plattsburgh International Airport | PBG | KPBG | 119,783 |
| Dutchess County Airport | POU | KPOU | 94 |
| Greater Rochester International Airport | ROC | KROC | 1,281,908 |
| Schenectady County Airport | SCH | KSCH | 46 |
| Adirondack Regional Airport | SLK | KSLK | 5,273 |
| Syracuse Hancock International Airport | SYR | KSYR | 1,139,568 |
| East 34th Street Heliport | TSS | N/A | |
| Oneida County Airport | UCA | KUCA | N/A |
Note: Passenger capacity figures are based on the latest available data and may vary annually.
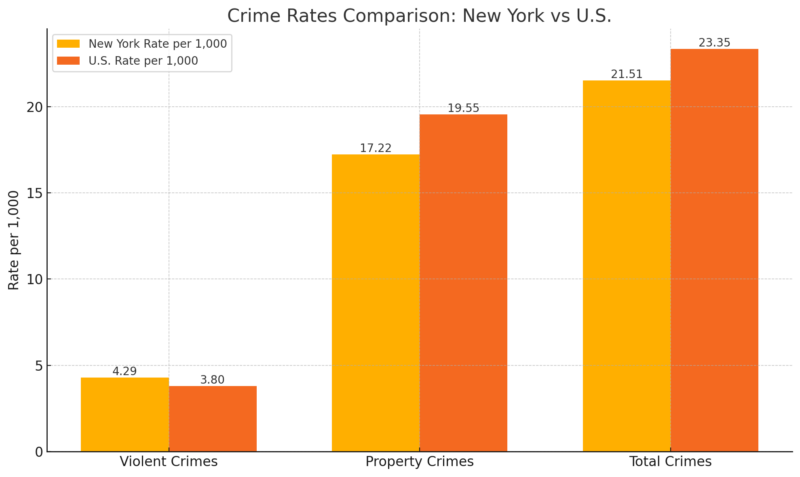
Crime Rate in New York
- Crime rates comparison – New York vs U.S. chart
Annual crime rate is 21.51 crimes per 1,000 residents, with violent crimes occurring at 4.29 per 1,000 residents and property crimes at 17.22 per 1,000 residents.
The chances of becoming a victim of violent crime in New York are 1 in 233, while for property crime, it’s 1 in 58. Violent crimes include 783 murders, 5,805 rapes, 22,040 robberies, and 55,841 assaults.
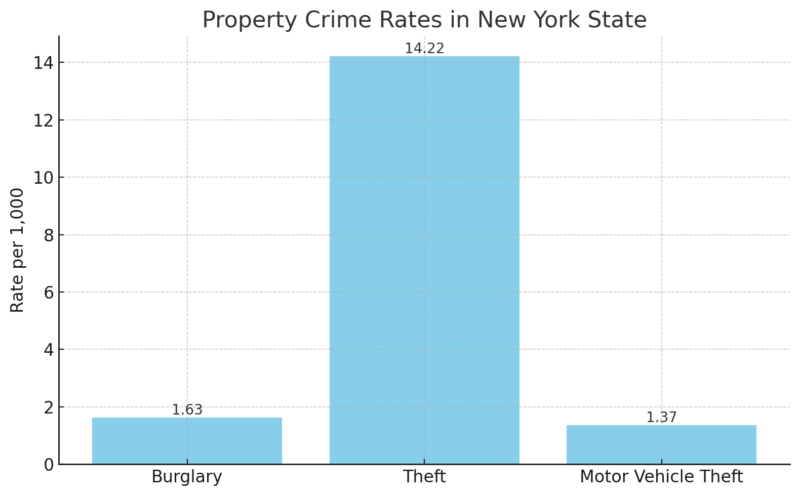
Property crimes comprise 31,976 burglaries, 279,810 thefts, and 26,971 motor vehicle thefts.
- Property crime rates in New York State chart
References:
- World Population Review – New York Population
- Census.gov – New York Population Change
- Department of Labor – New York State Geography
Related Posts:
- Map of New York City, New York – Geography,…
- Map of Texas - Cities, Geography, Counties & Stats (2025)
- Map of Pennsylvania - Cities, Geography, Counties &…
- Map of California - Cities, Geography, Counties &…
- Map of Colorado - Cities, Geography, Counties & Stats (2025)
- Map of Massachusetts - Geography, Cities, Counties &…