A recent study published in Nature Medicine reveals that dementia risks among Americans over the age of 55 are significantly higher than previously estimated.
Approximately 42% of this age group is projected to develop dementia later in life.
This alarming trend underscores the urgent need for enhanced public health initiatives.
Table of Contents
ToggleProjected Trends in Dementia Cases
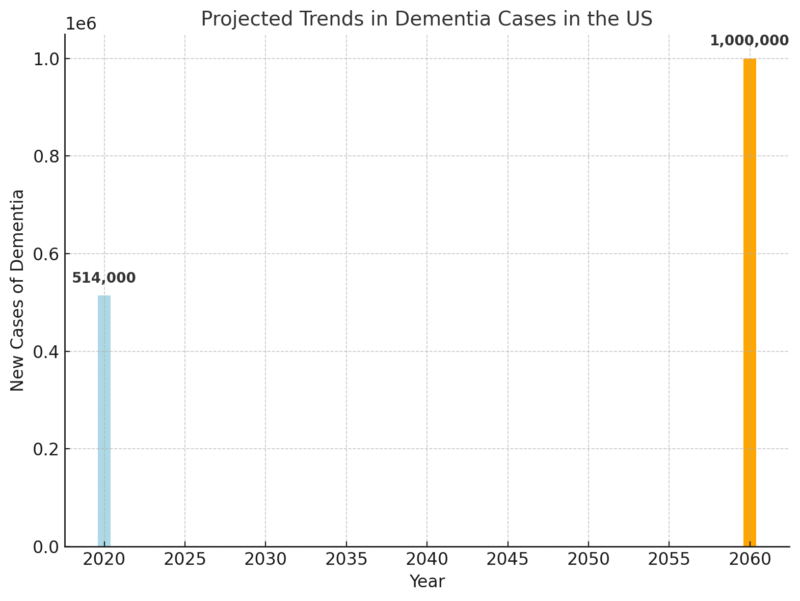
The doubling of dementia diagnoses over the next four decades is largely attributed to the aging Baby Boomer generation, with all Boomers reaching the high-risk age of 75 or older by 2040 according to Census.gov.
Demographic Insights
- Age-related Risk: Only 17% of dementia cases are diagnosed before age 75, with the average age of diagnosis being 81.
- Gender Disparity: Women face a higher lifetime risk of dementia (48%) compared to men (35%), mainly due to their longer life expectancy.
- Genetic Influence:
- APOE Gene: Individuals with two copies of the gene face a 59% risk, those with one copy face a 48% risk, and those with no copies face a 39% risk as noted by NCBI.
Racial and Socioeconomic Disparities
This study found that known risk factors explained about a third of #Alzheimer disease and related dementia cases, but with unequal distributions across racial and ethnic groups. Learn more: https://t.co/Gqqmlb66ek#NeuroTwitter pic.twitter.com/5e8PsnevqF
— Neurology Journal (@GreenJournal) January 29, 2024
The study revealed significant differences in dementia risks among racial groups:
- Black Adults: Higher rates of dementia and earlier onset compared to White adults.
- Future Trends: Dementia diagnoses among Black adults are projected to triple by 2060.
- Underlying Factors:
- Structural racism.
- Limited access to education, nutrition, and healthcare.
- Higher burden of vascular risk factors in midlife.
The shifting racial composition of the US population, with minority groups expected to constitute more than 50% by 2045, could also impact these trends.
Lifestyle and Preventative Opportunities
Nearly half of dementia cases could be delayed or prevented by addressing 14 key risk factors, such as maintaining a healthy diet, managing mental health, and addressing hearing loss. However, the current adoption of preventive measures remains low:
- Only 20% of adults meet cardiovascular and lifestyle health targets.
- Only 30% of older adults with hearing loss use hearing aids.
| Preventative Measures | Adoption Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| Healthy lifestyle behaviors | 20% |
| Hearing aid usage (for hearing loss) | 30% |
Advances in Diagnosis and Treatment
New diagnostic criteria from the Alzheimer’s Association emphasize the use of biomarkers for earlier and more accurate detection of dementia, particularly Alzheimer’s disease.
While novel treatments are on the horizon, clinical trials face challenges with insufficient racial diversity.
Call to Action
The study emphasizes the need for policies that:
- Promote healthy aging.
- Address health equity and structural disparities.
- Enhance prevention efforts, particularly among high-risk groups.
These steps are critical to mitigating the growing burden of dementia on individuals and the healthcare system.
Related Posts:
- Oregon’s Population Is Rising, but The Pace Has…
- Health Statistics and the Rising Costs of Personal…
- 15% of People Live Near Coasts – And the Number Keeps Rising
- Suicide Rising Among Gen Z - New Data Shows Young…
- Alcohol and Its Deadly Impact - U.S. Stats on…
- Bentonville Ignite Expansion And Its Long-Term…